
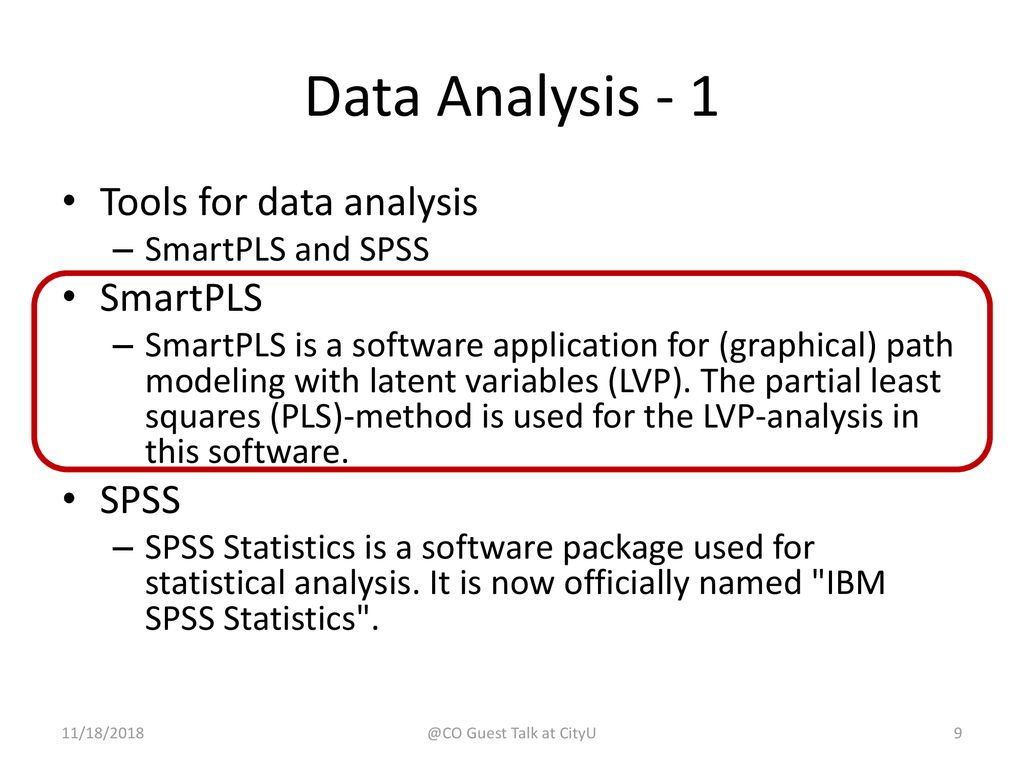
- #How to do exploratory data analysis in smartpls how to
- #How to do exploratory data analysis in smartpls free
So far, all of the data that you’ve seen has been tidy. “cell”, each variable in its own column, and each observation in its own Tabular data is tidy if each value is placed in its own Tabular data is a set of values, each associated with a variable and an An observation will contain several values,Įach associated with a different variable. (you usually make all of the measurements in an observation at the same Variable may change from measurement to measurement.Īn observation is a set of measurements made under similar conditions To make the discussion easier, let’s define some terms:Ī variable is a quantity, quality, or property that you can measure.Ī value is the state of a variable when you measure it. I’ll explain what variation and covariation are, and I’ll show you several ways to answer each question. The rest of this chapter will look at these two questions. What type of covariation occurs between my variables? What type of variation occurs within my variables? However, two types of questions will always be useful for making discoveries within your data. There is no rule about which questions you should ask to guide your research. You can quickly drill down into the most interesting parts of your data-and develop a set of thought-provoking questions-if you follow up each question with a new question based on what you find. On the other hand, each new question that you ask will expose you to a new aspect of your data and increase your chance of making a discovery. It is difficult to ask revealing questions at the start of your analysis because you do not know what insights are contained in your dataset. And like most creative processes, the key to asking quality questions is to generate a large quantity of questions. When you ask a question, the question focuses your attention on a specific part of your dataset and helps you decide which graphs, models, or transformations to make.ĮDA is fundamentally a creative process.
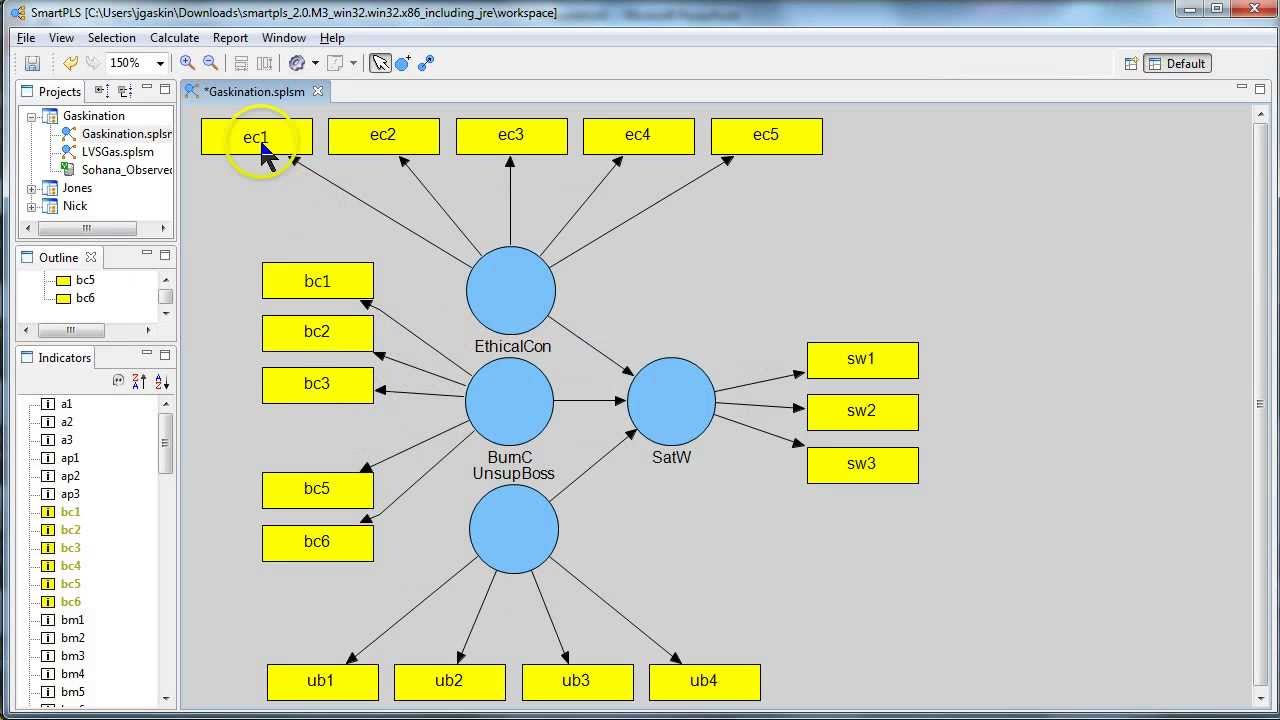
The easiest way to do this is to use questions as tools to guide your investigation. Your goal during EDA is to develop an understanding of your data. Vague, than an exact answer to the wrong question, which can always be made “Far better an approximate answer to the right question, which is often “There are no routine statistical questions, only questionable statistical To do data cleaning, you’ll need to deploy all the tools of EDA: visualisation, transformation, and modelling.

Data cleaning is just one application of EDA: you ask questions about whether your data meets your expectations or not. As your exploration continues, you will home in on a few particularly productive areas that you’ll eventually write up and communicate to others.ĮDA is an important part of any data analysis, even if the questions are handed to you on a platter, because you always need to investigate the quality of your data. Some of these ideas will pan out, and some will be dead ends.
#How to do exploratory data analysis in smartpls free
During the initial phases of EDA you should feel free to investigate every idea that occurs to you. More than anything, EDA is a state of mind.
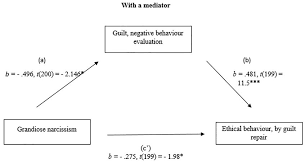
Use what you learn to refine your questions and/or generate new questions.ĮDA is not a formal process with a strict set of rules. Search for answers by visualising, transforming, and modelling your data.
#How to do exploratory data analysis in smartpls how to
This chapter will show you how to use visualisation and transformation to explore your data in a systematic way, a task that statisticians call exploratory data analysis, or EDA for short.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
